Your Shed Foundation: A Guide for Robust Construction
Last updated Thursday, September 19th, 2024

Choosing the right shed foundation is critical for the longevity and stability of your outdoor structure. In this guide, we’ll explore the types of shed foundations available and provide you with step-by-step instructions to ensure you make a solid and informed decision. Whether dealing with frost-proof options for colder climates, or seeking a quick on-grade solution, you’ll find the essential information you need without any fluff.
Key Takeaways
- Selecting the appropriate foundation is critical for shed longevity, with options like concrete blocks, gravel pads, pavers, or frost-proof constructions suited to different needs and climate conditions.
- Crucial considerations for a shed foundation include ensuring proper drainage, ground preparation, space around the structure, and planning for weight distribution to prevent future structural issues.
- Regular maintenance, including inspection for pests and repairs for any damage, ensures the longevity of the shed foundation, and adherence to local building codes and permits is essential for legal compliance.
Whether it's storage or an extra space to build things in, we're shed builders that make the most of your backyard space with a high-quality, long-lasting and durable shed or garage.
Understanding Shed Foundations: Types and Benefits
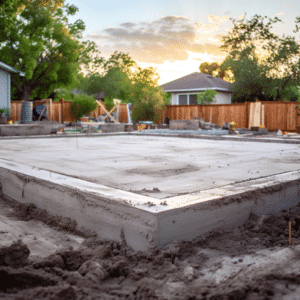
- Concrete block foundation: Provides strength and simplicity and is suitable for nearly all shed sizes, except the largest.
- Gravel pad foundation: Often recommended as the best foundation option due to its excellent drainage and leveling properties.
- Wood skid foundation: Uses pressure-treated lumber to create a sturdy base for your shed.
- Concrete slab foundation: Offers a solid and permanent base for your shed, but can be more expensive and time-consuming to install.
- Paver foundation: Uses interlocking pavers to create a stable and level surface for your shed.
Consider the specific needs of your shed and your budget when choosing the right foundation option for you.
Some popular choices for shed foundations include:
- Pressure-treated wooden skids or runners (often referred to as a skid foundation), also known as skid foundations
- Concrete footings with poles (pole-barn foundation)
- Metal shed jacks with adjustable height
- Timber-frame foundations, built using pressure-treated materials like 4x4s, 4x6s, or 6x6s
- Metal shed foundation kits, favored for their low price and simple design
For areas prone to erosion, a retaining wall-type base foundation can provide extra stability to safeguard your shed walls.
On-Grade Foundations
On-grade shed foundations are structures built on the ground surface or above the local area’s frost depth. They are known for their affordability and ease of installation when compared to frost-proof foundations. This makes them a popular choice for many homeowners. On-grade foundations come in various types, including deck block, skid, and timber frame, each offering distinctive features such as affordability, reusability, and acceptance of different flooring materials. These foundations are generally suitable for most small to medium-sized sheds and have the advantage of being movable if necessary.
For a solid on-grade foundation, it’s advisable to:
- Use solid-concrete blocks instead of hollow ones
- Clear away the grass under each block, enhancing stability
- Compact crushed stone under each block to further enhance the foundation’s stability.
On-grade foundations, whether they are made of concrete blocks or wood frame, provide a solid foundation for a shed while allowing flexibility in location and flooring options.
Frost-Proof Foundations
Frost-proof foundations are beneficial in cold-weather regions as they can support more weight and prevent shifting during temperature fluctuations and frost heaves, especially in areas with silty or sandy soil. Unlike on-grade shed foundations, which are suitable for areas with little to no frost, frost-proof shed foundations are essential in regions that experience deep ground freezing and frost heaving.
Soil conditions significantly influence the design of frost-proof foundations. For instance, the presence of expansive clays requires special construction techniques to mitigate the soil’s retention of water and tendency to expand. Building a frost-proof foundation involves:
- Placing structural units like concrete piers or footings beneath the frost line
- The frost line is typically 30 inches deep in Maryland
- Guarding against freeze-thaw cycle-induced heaving
Combination Foundations
Combination shed foundations incorporate elements of both on-grade and frost-proof foundations, enhancing their versatility for different environmental conditions. By combining a gravel base with strategically placed concrete piers, these foundations can become frost-resistant and cost-effective compared to full concrete pad foundations.
The installation method can be adapted to make combination foundations either into a permanent foundation or removable, providing flexibility based on the shed owner’s needs. Moreover, combination foundations enhance structural integrity by preventing settling and keeping the shed level, which helps mitigate moisture problems over time.
Essential Factors to Consider When Choosing a Shed Foundation
The longevity and performance of your shed hinges on the vital decision of selecting the appropriate foundation. There are several essential factors to consider when choosing a shed foundation. First, a good drainage is crucial to prevent structural strain or flooding, especially for a gravel pad foundation. Second, inadequate ground preparation can lead to uneven settling over time, which can strain the shed’s framing, leading to potential issues such as doors and windows binding.
Thirdly, not preparing enough extra space around the shed foundation can lead to moisture issues and deterioration due to rainwater splashback and weed growth. Using landscape fabric in ground preparation helps prevent weed growth and adds stability to the foundation by separating the gravel from the soil. Creating a perimeter for the shed foundation ground prep can prevent soil and gravel spread, ensuring stability even on sloped ground.
Finally, the number of piers required for a shed foundation varies according to shed size and the weight of items stored, requiring careful planning for weight distribution.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building Various Shed Foundations
Having discussed the various shed foundation types and the considerations for choosing the right one, we will now venture into the practical aspects of the construction process. Whether you’re planning on a gravel pad, concrete block, paver, post-and-beam, or concrete pier foundation, a step-by-step guide can be invaluable.
Let’s walk through each of these foundation types to understand the building process in detail.
Gravel Pad Foundation
The first step in constructing a gravel pad foundation is to ascertain a level surface. Remove any topsoil, and compact the ground beneath. A final check for levelness using a spirit level or laser level followed by compacting the base ensures a stable foundation. For the gravel pad itself, use a minimum of 4 inches of ¾ inch clean stone. It’s recommended to extend the gravel base 6 inches deep and one foot beyond shed dimensions on all sides. Using stabilization fabric can prevent weed growth and maintain stability.
A gravel pad foundation offers several advantages:
- It’s cost-effective and offers ease of installation
- It provides better drainage compared to flat concrete pads
- It can solve issues in unlevel areas by extending the gravel further on the lower side.
When building the gravel pad for gravel foundations, outline the area with stakes and string, ensure it is perfectly level for the stability of the foundation, and firmly tamp the gravel to lock it in place.
Concrete Block Foundation
The process of building a concrete block foundation involves confirming the levelness of all blocks and offering robust support for the shed floor to prevent shifts or settlement. Start by selecting a site with good drainage and minimal slope. Ensure to clear the area of obstructions like tree branches or power lines beforehand. Layout the area for the concrete blocks by hammering wooden stakes into each corner, running a string outline around these stakes, and checking the layout is square with a level.
To create a sturdy foundation for your shed, follow these steps:
- Place solid concrete blocks flush inside the string perimeter.
- For each block, excavate grass and soil to make room for gravel beneath and level the blocks with gravel underneath.
- If the site slopes, use concrete blocks of varying thicknesses, such as 2-, 4-, or 8-inch blocks, to raise the foundation’s lower end to match the higher end, ensuring a level foundation.
- Once the concrete blocks are set and properly spaced, the foundation is ready for the shed floor frame construction.
- This raised base protects against moisture, providing a strong foundation for your shed.
Paver Foundation
Comprising pavers laid out on a level plane, a paver foundation offers straightforward installation but is vulnerable to frost heave and soil expansion. For a stable paver foundation, it’s crucial to perform careful ground leveling and to utilize sand or fine gravel as a base beneath the pavers to ensure a secure fit.
The installation of paver foundations requires that pavers be tightly interlocked to maintain the integrity of the foundation, with edge restraints used to preserve paver alignment and prevent spreading from traffic or heavy loads. The cost for constructing a paver foundation can range from $200 – $1,000, varying based on size and materials.
A paver foundation not only provides stability but also enhances the aesthetic appeal of the outdoor space, making it a popular choice for many homeowners.
Post-and-Beam Foundation
The construction of a post-and-beam foundation involves the following steps:
- Start by marking the layout with stakes and ensuring squareness.
- Set a string guide to determine slope.
- Pour concrete footers.
- Place pressure-treated posts into the holes.
These steps will help you create a stable base for the shed’s flooring.
Once posts are squared and plumbed, they should be aligned, leveled, and secured by filling holes with concrete and tamping. Support beams made of double 2×10 inch boards are then:
- nailed together
- through-bolted to the posts
- joists are added between beams secured with hanger ties
- lateral braces for extra stability
This type of foundation is ideal for sloped build sites, allowing fewer concrete footings and creating an elevated foundation that helps resist contact with wet ground.
Concrete Pier Foundation
A concrete pier foundation is constructed by:
- Digging holes to the local frost line
- Adding 4”-6” of gravel base
- Ensuring piers rise at least 6” above ground
- Placing concrete (for instance, using Sonotube® forms for slopes)
- Using adjustable post bases to achieve a level foundation after the concrete sets
- After the piers are set and the concrete has cured, you can construct a wooden frame or attach a metal bracket system on top of the pier posts to support the shed structure.
Concrete piers offer frost-proofing advantages, making them suitable for areas with freeze-thaw cycles and providing a durable, long-lasting shed foundation. During the pouring of concrete piers, incorporating anchoring hardware can add extra stability and strength to the shed foundation. Concrete piers reinforced with vertical 4×4 posts tied to a skid foundation using carriage bolts create a robust anchor against wind uplift, enhancing the shed’s resistance to extreme weather.
DIY vs. Hiring a Professional: Pros and Cons

- Full control over the construction process
- Customization with flexible material and design options
- A sense of personal accomplishment
- Cost-effective choice, saving you the expenses of hiring a contractor
- An educational experience, equipping you with skills for future projects.
However, there are also potential downsides to consider. DIY shed foundation projects often require more time than professional installations, potentially delaying the overall project timeline. Building without a required permit can lead to:
- substantial fines
- property tax reassessment
- difficulties in selling or refinancing a home
- the potential need to remedy the work retrospectively
It is important to weigh these factors before deciding to proceed with a DIY shed foundation project.
On the other hand, hiring a professional contractor brings expertise to the project, ensuring the shed foundation is built to meet code standards and with high-quality workmanship. Professionals also provide warranties or guarantees for their work, offering protection against material and construction defects.
Shed Foundation Maintenance Tips
Maintaining a well-constructed shed foundation regularly is vital for keeping it in an optimal state. Proper drainage around the shed foundation is essential to prevent moisture damage. The ground should slope away from the shed to avoid water pooling. In the case of water buildup issues, the installation of a gravel base foundation is beneficial for its absorbent and draining properties.
Regular inspections for termite or carpenter ant infestations are crucial as these pests can undermine structural integrity. Using repellent lining paper inside the shed serves as a physical barrier to prevent bugs from nesting or feeding on shed materials. To maintain the foundation, keep the area free of debris and foliage to reduce dampness and airflow restrictions which can attract pests.
If signs of bug activity are detected, act quickly by utilizing safe and appropriate insecticides or remedies. Address any cracks found in concrete foundations by using the correct concrete repair products, considering weather conditions for proper set. An uneven gravel shed foundation can be re-leveled by adding more gravel to maintain a solid base for the shed.
Customizing Your Shed Foundation
The purpose of your shed foundation need not be purely practical. Numerous opportunities for customization exist to amplify its aesthetics and functionality. For example, landscaping around the shed foundation with decorative stones and plants can create a more visually appealing and cohesive garden look. For improved accessibility, especially for foundations that are above ground level, installing steps or ramps can be an essential customization.
Creating a raised floor system allows for built-in storage solutions such as shelving units or drawers beneath the shed. Considering the shed’s intended use, such as for storage or as a workshop, will influence the need for durability and may necessitate the inclusion of electrical conduits or plumbing in the foundation design.
Customizing the foundation to attach additional structures like a greenhouse or potting bench can create a versatile space for hobbies such as gardening. You can even install roofing felt on the shed foundation for added protection against pests and to help regulate temperature and humidity within the shed.
Local Building Regulations and Permits
Creating a shed foundation extends beyond merely selecting suitable materials and assembling them. It also encompasses aligning your project with local building rules and regulations. Securing a building permit is essential to prevent potential legal troubles down the line. Local regulations may stipulate specific requirements for shed foundations, such as size exemptions, necessary setbacks from property lines, and additional mandates for sheds used in business operations.
The permit process typically involves submitting a plot diagram and building plans, undergoing any required inspections, and paying fees that range from approximately $50 to $250. Building without a required permit can lead to substantial fines and property tax reassessment, difficulties in selling or refinancing a home, and the potential need to remedy the work retrospectively. It’s always a good idea to consult your local building department to understand the specific regulations and requirements that apply to your project.
Shed Foundation Troubleshooting: Common Problems and Solutions
Despite a well-constructed shed foundation promising to offer a robust platform for your shed for numerous years, complications can occasionally crop up. For example, uneven settling of the shed foundation can be corrected by adjusting the material under the foundation blocks or supports to re-level the foundation. A shed foundation that has shifted from factors such as heavy wind or foot traffic can be repaired by re-leveling the ground and ensuring the base is compacted and stable.
Metal shed jack foundations are vulnerable to soil movement and frost heave, and might not conform to local building codes; adjustments or alternative foundation solutions might be necessary. A combination of prevention and correction methods can solve most common shed foundation problems:
- Ensure proper ground leveling
- Opt for a gravel foundation
- Allow extra perimeter space
- Use landscape fabric
- Construct a solid wooden perimeter
Preparing Your Shed for Extreme Weather Conditions
Extreme weather conditions can pose a significant challenge to your shed and its foundation. Elements like heavy rain, snow, high winds, and drastic temperatures can exert substantial stress on a shed. Therefore, it’s crucial to prepare your shed foundation for these challenges. One of the ways to do this is by considering the local climate when choosing your foundation type. For instance, in areas with freeze-thaw cycles, a frost-proof foundation like a gravel pad with proper footers can meet local municipality requirements and withstand the climate challenges.
Severe weather conditions can also impact local building codes, which in turn can influence the construction requirements for shed foundations, including aspects such as anchoring. Therefore, preparing your shed for extreme weather conditions isn’t just about the initial construction—it’s also about ongoing maintenance and compliance with local building codes. From checking for damage after a storm to ensuring proper anchoring, preparation can help your shed and its foundation withstand the elements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best foundation for a shed?
A gravel pad foundation made with crushed stone is the best choice for a shed foundation as it is inexpensive, stable, and easy to build.
What is the cheapest way to build a shed foundation?
The cheapest way to build a shed foundation is by using gravel. It is cost-effective and can be easily installed by individuals with basic DIY skills, without requiring professional assistance.
Do you need a foundation under a shed?
Yes, it’s important to have a foundation under a shed to keep it level, protect it from moisture, and ensure its stability and longevity. Both concrete slabs and gravel bases are popular options for creating a sturdy foundation.
Does a 10x10 shed need a foundation?
Yes, a 10×10 shed would benefit from a foundation for protection and extended useability. Consider installing one for better durability and functionality.
What are the different types of shed foundations?
There are various types of shed foundations, such as on-grade, frost-proof, and combination foundations, each offering different options like deck block, skid, timber frame, concrete block, gravel pad, paver, post-and-beam, and concrete pier foundations.
Built for Your Life, and All the Things That Come With It
Whether it’s storage or a extra space build things in, we’re shed builders that make the most of your backyard space with a high quality, long-lasting and durable shed.
Quote Your Shed or text / call 757-663-8470

